Atmospheric particulate matter in Tarnów City (Southern Poland) – short time investigation of a space-time variability in the winter of 2019
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5604/01.3001.0013.2884Keywords:
airborne pollution, particulate matter, heating season, smogAbstract
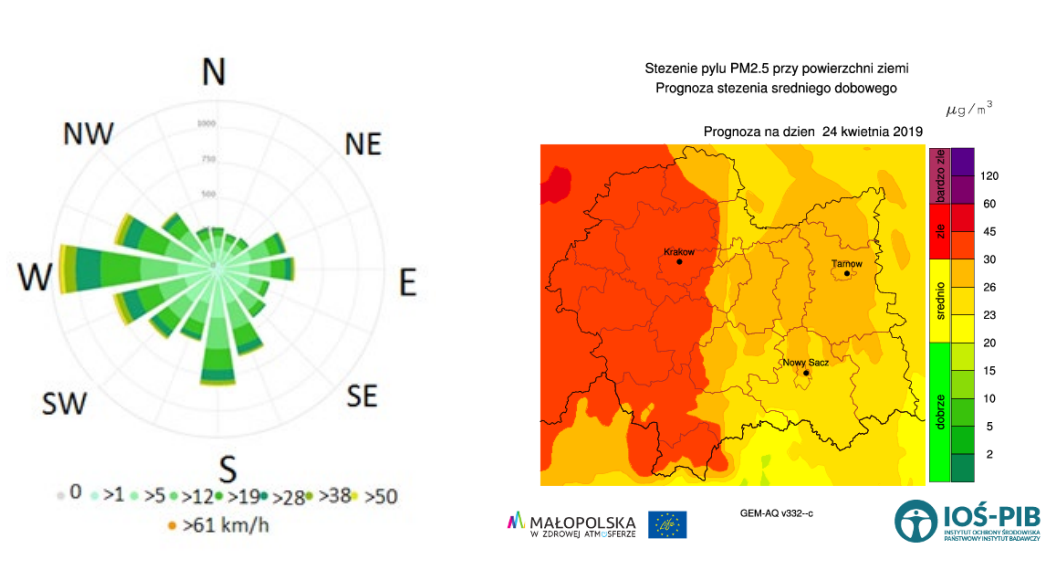
Tarnów is a city where air pollution is a major problem during the wintertime. An acceptable level of PM2.5 and PM10 concentrations are exceeded very often. The main reason of this situation is individual housing and their heat system based on ineffective old units based on hard coal and sometimes even people use waste as a fuel. The city has two air quality monitoring stations and a private network for measurements of particulate matter. However, there is still a lack of information on air quality in some areas of the city. For obtaining full information on the air quality in Tarnów, readings from the monitoring station and field measurements were carried out. The obtained information allowed to determine which areas of the city are most exposed to the occurrence of smog in the heating season. So far, air quality measurements in Tarnów have not been conducted at the same time for so many collections.The most polluted air occurs in Krzyż District but air quality should be improved in all city. The best air quality has been observed for locations where heat is available from municipal heating plant e.g. Słoneczna Str. Presented research work shows that air quality in Tarnów City is very unhealthy because of particulate matter pollution. In the winter time the main problem is too high concentration of PM2.5, but also PM10 concentration. Those parameters are very frequently exceeded. The worst air quality occurs in the evenings (8 p.m.), but in the mornings (8 a. m.) air quality is highly polluted too. When air quality in Tarnów City is bad situation concerns all localisations. The similar situation is observed when air quality is good or acceptable. The main conclusion is that for locations where heat is available from heat plant is not generated individually by domestic sources, the situation is the most comfortable. Our investigation covered short period, but it is preliminary study and this important issue will be continued in the future.
Downloads
References
Kosarz M, Satora P. Związki odpowiedzialne za zanieczyszczenie powietrza. Ecological Engineering. 2017;18: 89-95. doi: https://doi.org/10.12912/23920629/79820. Google Scholar
Zielińska E, Wielgus A, Dreliszak J, Zukow W. Air pollution – selected health effect in Poland. Journal Education, Health and Sport. 2018; 8:641-648. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.2527086. Google Scholar
Zhang N, Li M, Qian J, Wang Q, Zhao J, Yang Z, Tian Z, Zhang X, Zuo X, Zhang M, Zhu P, Ye S, Zhang W, Zhang Y, Qi W, Li Y, Zhang Z, Ding F, Gu J, Liu Y, Wei W, Zheng X. Pulmonary arterial hypertension in systemic lupus erythematosus based on a CSTAR-PAH study: Baseline characteristic and risk factor. International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases. 2019;22:921–928. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/1756-185X.13478. Google Scholar
Bruckmann P, Hiester E, Kless M, Zetzsch C. Trends of PCDD/F and PCB concentrations and depositions in ambient air in Northwestern Germany. Chemosphere. 2013;93:1471–1478. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere. 2013.07.029. Google Scholar
Szczerbowski R. Wyzwania polskiego sektora wytwórczego do 2030 roku. Zeszyty Naukowe Instytutu Gospodarki Surowcami Mineralnymi i Energii PAN. 2018;102:203–216. Google Scholar
Dz.U. 2002 nr 87, poz. 796: Rozporządzenie Ministra Środowiska z dnia 6 czerwca 2002 r. w sprawie dopuszczalnych poziomów niektórych substancji w powietrzu, alarmowych poziomów niektórych substancji w powietrzu oraz marginesów tolerancji dla dopuszczalnych poziomów niektórych substancji. Google Scholar
Dz.U. 2012, poz. 1031: Rozporządzenie Ministra Środowiska z dnia 24 sierpnia 2012 r. w sprawie poziomów niektórych substancji w powietrzu. Google Scholar
Dz.U. 2018, poz. 1119: Rozporządzenie Ministra Środowiska z dnia 8 czerwca 2018 r. w sprawie dokonywania oceny poziomów substancji w powietrzu. Google Scholar
Touray N, Chyc M. Fuel modification based on some metals compounds and their environmental impact. Science, Technology and Innovation. 2018;2:1-6. doi: https://doi.org/10.5604/01.3001.0012.1152. Google Scholar
Matuszkiewicz JM. Potencjalna roślinność naturalna Polski, IGiPZ PAN, Warszawa, 2008. Google Scholar
S.G. 2018: Statistical guidbook 2018. Urząd Statystyczny, Kraków 2018. Google Scholar
https://airly.eu/pl/, (access: 1.03.2019). Google Scholar
https://pl.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tarn%C3%B3w, (access: 29.11.2017). Google Scholar
http://geoserwis.gdos.gov.pl, (access 29.11.2017). Google Scholar
http://geoserwis.gdos.gov.pl, (access: 29.11.2017). Google Scholar
WIOŚ: http://monitoring.krakow.pios.gov.pl/ (access: 1.03.2019). Google Scholar
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2019 University of Applied Sciences in Tarnow, Poland & Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.



