Fabrication, properties and cytotoxicity evaluation of degradable poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-lactide) for the use as nerve guidance channels
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5604/01.3001.0010.7999Słowa kluczowe:
peripheral nerve regeneration, degradable polymer, PTMC/PLA, contact angle, roughness, morphology, viability, fibroblastsAbstrakt
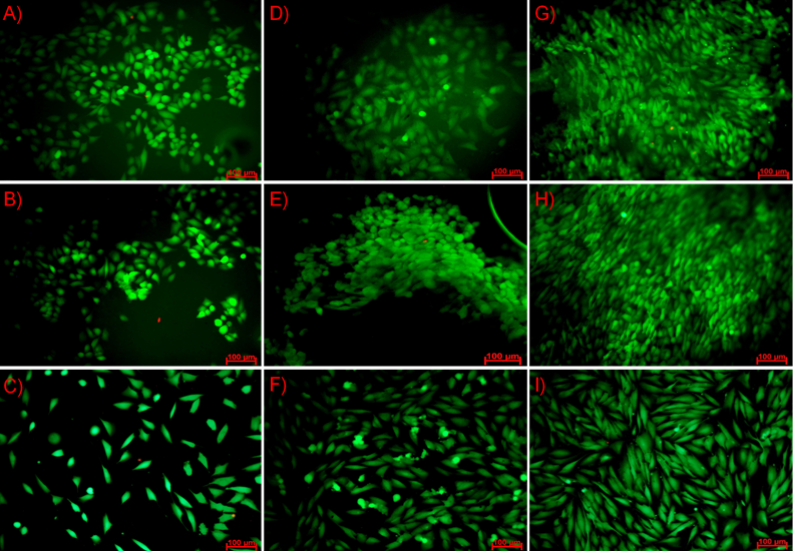
Strategies to improve healing of damaged nerves include the application of specialized nerve guides, which hold the promise for allowing reanastomosis of the severed or damaged fibers. Studies have demonstrated that the use of a slowly degradable polymeric nerve guide can improve the nature and rate of nerve regeneration across a short gap in small nerves. The objective of this study was to characterize a biodegradable nerve guide based on poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-lactide) for peripheral nerve regeneration and to evaluate its cytotoxicity. The obtained copolymer films were incubated in two different media (distilled water and simulated body fluid), and while the degradation process appeared, pH and ion conductivity changes of solutions were monitored as well as mass loss of the samples. Additionally, mechanical tests (tensile strength, elongation at break and Young’s modulus parameters) before and after different time points were carried out. To evaluate cytotoxicity biological test were done on fibroblasts cells (NIH 3T3). Cell metabolic activity was determined using Alamar Blue reagent and their morphology was observed under fluorescence microscopy. The growth of pH in both media were mostly caused by steadily degradation of carbonate units into alkaline diols. The growth of ion conductivity value at the beginning of the incubation process was associated with the releasing of free ions to the solution. The mechanical parameters decreased with the progress of degradation process. Ringer’s fluid, as more aggressive, caused higher decrease in mechanical properties. The measured contact angles showed good surface wettability. Both surfaces, the top and the bottom, had similar hydrophilicity. Moreover, activity of fibroblasts cells were similar on both sides as well as on the reference TCPS. Good adhesion of NIH 3T3 cells to the surface suggests that the hydrophilic polymers promote colonization of fibroblasts cells on their surface. Biological studies have shown that used cells are very sensitive to surface topography which they colonize and cell viability was higher at the bottom surface, which has a slightly higher average roughness Ra. Thus, fibroblasts cell preferred colonizing rougher than smoother surfaces. Fabricated films does not affect negatively, namely, toxic on cell cultures and forms substrate with favourable surface properties. This was confirmed by the Alamar Blue tests and microscopic observations.
Statystyka pobrań
Bibliografia
A. Faroni, S. A. Mobasseri, P. J. Kingham and A. J. Reid, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev., 2015, 82, 160–167. Google Scholar
A. M. Moore, R. Kasukurthi, C. K. Magill, H.F. Farhadi, G. H. Borschel and S. E. Mackinnon, HAND, 2009, 4, 180–186. Google Scholar
S. E. Mackinnon and A. L. Dellon, Plast. Reconstr. Surg., 1990, 85, 419–24. Google Scholar
G. R. Evans, Anat. Rec., 2001, 263, 396–404. Google Scholar
M. F. Meek, K. Jansen, R. Steendam, W. van Oeveren, P. B. van Wachem and M. J. a van Luyn, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A, 2004, 68, 43–51. Google Scholar
A. Berger, F. Lassner and E. Schaller, Handchir. Mikrochir. Plast. Chir., 1994, 26, 44–7. Google Scholar
W. A. Crawley and A. L. Dellon, Plast. Reconstr. Surg., 1992, 90, 300–2. Google Scholar
J. Kim and A. L. Dellon, J. Foot Ankle Surg., 2001, 40, 318–23. Google Scholar
M. F. Meek and J. H. Coert, J. Reconstr. Microsurg., 2002, 18, 97–109. Google Scholar
K. Matsumoto, K. Ohnishi, T. Kiyotani, T. Sekine, H. Ueda, T. Nakamura, K. Endo and Y. Shimizu, Brain Res., 2000, 868, 315–328. Google Scholar
T. Nakamura, Y. Inada, S. Fukuda, M. Yoshitani, A. Nakada, S. I. Itoi, S. I. Kanemaru, K. Endo and Y. Shimizu, Brain Res., 2004, 1027, 18–29. Google Scholar
T. Kiyotani, M. Teramachi, Y. Takimoto, T. Nakamura, Y. Shimizu and K. Endo, Brain Res.,1996, 740, 66–74. Google Scholar
S. C. Park, S. H. Oh, T. B. Seo, U. Namgung, J. M. Kim and J. H. Lee, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. - Part B Appl. Biomater., 2010, 94, 359–366. Google Scholar
X. Wen and P. A. Tresco, Biomaterials, 2006, 27, 3800–3809. Google Scholar
R. Sasaki, S. Aoki, M. Yamato, H. Uchiyama, K. Wada, H. Ogiuchi, T. Okano and T. Ando, J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med., 2011, 5, 823–830. Google Scholar
S. H. Oh and J. H. Lee, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A, 2007, 80A, 530–538. Google Scholar
A. L. Luis, J. M. Rodrigues, S. Amado, A. P. Veloso, P. A. S. Armada-Da-silva, S. Raimondo, F. Fregnan, A. J. Ferreira, M. A. Lopes, J. D. Santos, S. Geuna, A. S. P. Varejão and A. C. Maurício, Microsurgery, 2007, 27, 125–137. Google Scholar
S. Hsu and H.-C. Ni, Tissue Eng. Part A, 2009, 15, 1381–1390. Google Scholar
V. Maquet, D. Martin, B. Malgrange, R. Franzen, J. Schoenen, G. Moonen and R. Jereme, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., 2000, 52, 639–651. Google Scholar
H. Steuer, R. Fadale, E. Müller, H.-W. Müller, H. Planck and B. Schlosshauer, Biohybride nerve guide for regeneration: degradable polylactide fibers coated with rat Schwann cells, 1999, vol. 277. Google Scholar
F. J. Rodríguez, N. Gómez, G. Perego and X. Navarro, Biomaterials, 1999, 20, 1489–1500. Google Scholar
M. Vert, S. M. Li, G. Spenlehauer and P. Guerin, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med., 1992, 3, 432–446. Google Scholar
A. G. M. Lu, Lichun, Charles A. Garcia, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., 1999, 46, 236–244. Google Scholar
A. R. Katz, D. P. Mukherjee, A. L. Kaganov and S. Gordon, Surg. Gynecol. Obstet., 1985, 161, 213–22. Google Scholar
C. G. Pitt, M. Chasin, A. Domb, E. Ron, E. Mathiowitz, R. Langer, K. Leong, C. Laurencin, H. Brem and S. Grossman, Biodegrad. Polym. as Drug Deliv. Syst., 1990, 71–120. Google Scholar
A. P. Pêgo, M. J. A. Van Luyn, L. A. Brouwer, P. B. van Wachem, A. A. Poot, D. W. Grijpma and J. Feijen, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., 2003, 67A, 1044–1054. Google Scholar
A. P. Pêgo, A. A. Poot, D. W. Grijpma and J. Feijen, Macromol. Biosci., 2002, 2, 411–419. Google Scholar
Z. Zhang, R. Kuijer, S. K. Bulstra, D. W. Grijpma and J. Feijen, Biomaterials, 2006, 27, 1741–1748. Google Scholar
A.-C. Albertsson and M. Eklund, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 1995, 57, 87–103. Google Scholar
K. J. Zhu, R. W. Hendren, K. Jensen and C. G. PITT, Macromolecules, 24, 1736–1740. Google Scholar
T. Tyson, A. Finne-Wistrand and A.-C. Albertsson, Biomacromolecules, 2009, 10, 149–154. Google Scholar
Y. Qin, M. Yuan, L. Li, S. Guo, M. Yuan, W. Liand J. Xue, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater., 2006, 79B, 312–319. Google Scholar
Z. Zhang, D. W. Grijpma and J. Feijen, Macromol. Chem. Phys., 2004, 205, 867–875. Google Scholar
A. P. Pêgo, A. A. Poot, D. W. Grijpma and J. Feijen, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med., 2003, 14, 767–773. Google Scholar
H. Tian, Z. Tang, X. Zhuang, X. Chen and X.Jing, Prog. Polym. Sci., 2012, 37, 237–280. Google Scholar
A. Södergård and M. Stolt, Prog. Polym. Sci., 2002, 27, 1123–1163. Google Scholar
L. S. Nair and C. T. Laurencin, Prog. Polym. Sci., 2007, 32, 762–798. Google Scholar
A. P. Gupta and V. Kumar, Eur. Polym. J., 2007, 43, 4053–4074. Google Scholar
N. Murthy, S. Wilson and J. C. Sy, Polym. Sci. A Compr. Ref. 10 Vol. Set, 2012, 9, 547–560. Google Scholar
S. Wang and L. Cai, Int. J. Polym. Sci., 2010, 2010. Google Scholar
H. K. Moon, Y. S. Choi, J. K. Lee, C. S. Ha, W. K. Lee and J. A. Gardella, Langmuir, 2009, 25, 4478–4483. Google Scholar
Z. Ma, Z. Mao and C. Gao, Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces, 2007, 60, 137–157. Google Scholar
H.-I. Chang and Y. Wang, Regen. Med. Tissue Eng. - Cells Biomater., 2011, 569–588. Google Scholar
A. Khalili and M. Ahmad, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2015, 16, 18149–18184. Google Scholar
Pobrania
Opublikowane
Jak cytować
Numer
Dział
Licencja
Prawa autorskie (c) 2017 Państwowa Wyższa Szkoła Zawodowa w Tarnowie & Autor

Utwór dostępny jest na licencji Creative Commons Uznanie autorstwa – Użycie niekomercyjne 4.0 Międzynarodowe.



