Meteomodem M20 radiosonde as a radio tracker with amateur software
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55225/sti.700Keywords:
stratospheric balloon, radiosonde, Meteo modem, M20, ADF7012, Horus, 4FSKAbstract
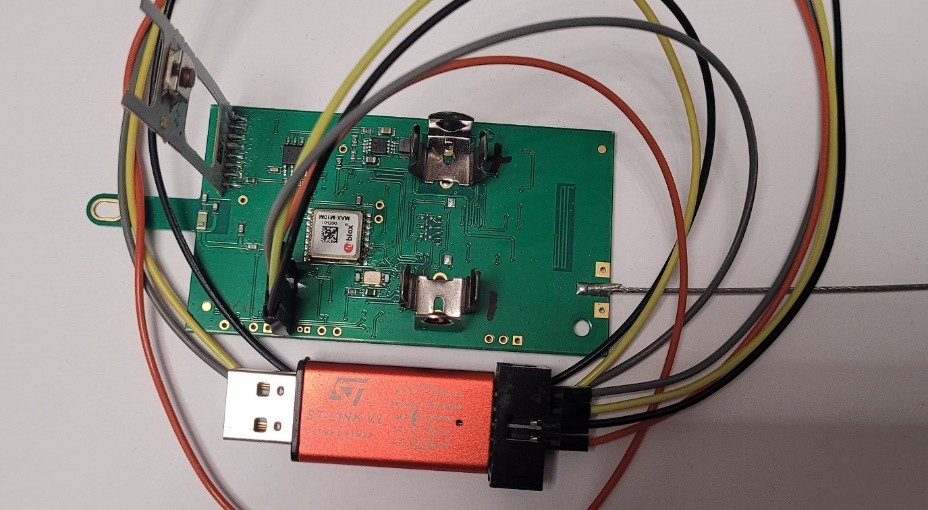
This article describes the software for factory-installed Meteomodem M20 radiosondes operating in the Horus V2 standard. Developed by the AMPER Student Research Group for Electronics at the University of Tarnów, this version of the program runs on a recovered meteorological probe and requires no additional modifications (e.g., microcontroller replacement). Due to severely limited resources (the original microcontroller has only 32kB of Flash memory), the Keil package was used for compilation. This commercial software is available, but for L0 series processors, the package is free; its use requires only prior registration. The software was tested in three consecutive balloon missions. In the BEM 1 mission, a probe was sent with software transmitting in the RTTY standard, while in the BEM 2 and BEM 3 missions, the software described in the article was tested operating in the Horus V2 standard.
Downloads
References
Antosz J, Arabik R, Jasielski J, Witek M, Ciężadło Ł. Misje stratosferyczne Akademii Tarnowskiej: część 1: sprzęt i oprogramowanie. Science, Technology and Innovation. 2023;18(3–4):30-45. https://doi.org/10.55225/sti.565. DOI: https://doi.org/10.55225/sti.565 Google Scholar
Krahn T. PecanPico4 [Internet]. GitHub; c2025 [cited 2025 Nov 30]. Available from: https://github.com/tkrahn/pecanpico4. Google Scholar
Kroes R. HorusBinary Tracker [Internet]. GitHub; c2025 [cited 2025 Nov 30]. Available from: https://github.com/RoelKroes/HorusBinary_Tracker Google Scholar
Nousiainen M. RS41ng [Internet]. GitHub; c2025 [cited 2025 Nov 30]. Available from: https://github.com/mikaelnousiainen/RS41ng Google Scholar
Versatile, feature-rich and user-friendly custom firmware for ALL revisions of Vaisala RS41 radiosondes [Internet]. GitHub; c2025 [cited 2025 Nov 30]. Available from: https://github.com/Nevvman18/rs41-nfw Google Scholar
Analog Devices. ADF7012 [Internet]. c2025 [cited 2025 Nov 30]. Available from: https://www.analog.com/en/products/adf7012.html Google Scholar
Blitzortung.org. GlobalTop FlashTool [Internet]. c2025 [cited 2025 Nov 30]. Available from: https://www.blitzortung.org/Compendium/Hardware/GlobalTop/GlobalTop%20FlashTool%20lightningmaps_org/ Google Scholar
STMicroelectronics. STM32Cube initialization code generator (STM32CubeMX) [Internet]. c2025 [cited 2025 Nov 30]. Available from: https://www.st.com/en/development-tools/stm32cubemx.html Google Scholar
Project Horus Team. Project Horus [Internet]. c2025 [cited 2025 Nov 30]. Available from: http://www.projecthorus.org/ Google Scholar
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Jacek Jasielski, Maciej Witek

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.



