Rola NASA w monitorowaniu ozonu stratosferycznego. Czy działania dotyczące ochrony warstwy ozonowej są skuteczne?
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55225/sti.697Słowa kluczowe:
zubożenie warstwy ozonowej, monitorowanie warstwy ozonowej, misje kosmiczne, przepisy międzynarodoweAbstrakt
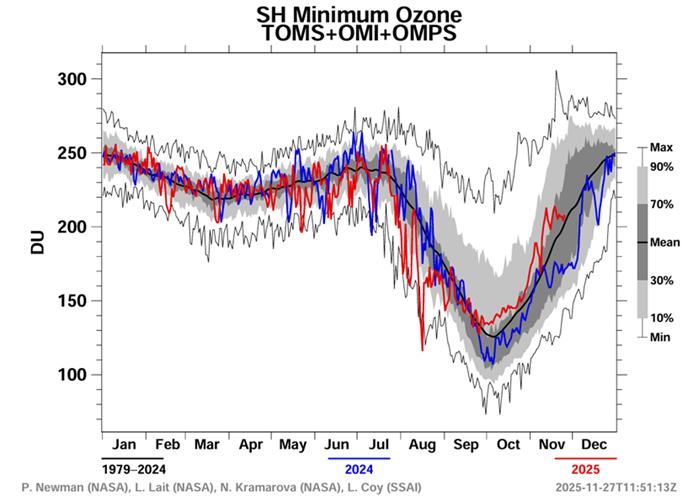
Stratosferyczna warstwa ozonowa (10–50 km) pochłania biologicznie szkodliwe promieniowanie ultrafioletowe, umożliwiając przetrwanie życia na Ziemi. Wczesne pomiary NASA z lat 60. i 70. XX wieku wykazały, że naturalny poziom ozonu jest kontrolowany przez śladowe ilości tlenków azotu, tlenków wodoru i halogenów. Około 20 misji NASA, wraz z NOAA, ESA i innymi partnerami międzynarodowymi, przyczyniło się do globalnego monitoringu ozonu. Obserwacje ujawniły poważne wiosenne zubożenie warstwy ozonowej nad Antarktydą w latach 1984–1985. NASA odnotowała najniższą wartość ozonu w historii pomiarów nad biegunem południowym – 73 DU 30 września 1994 r. – oraz największą jednodniową dziurę ozonową o rozmiarze 29,9 · 10⁶ km² 9 września 2000 r. Protokół montrealski (1987) doprowadził do 99-procentowego wycofania regulowanych substancji zubożających warstwę ozonową. Według najnowszej oceny WMO/UNEP, warstwa ozonowa powróci do poziomu z 1980 roku około 2066 roku nad Antarktydą, 2045 roku nad Arktyką i 2040 roku na całym świecie, zakładając, że obecne środki kontroli pozostaną w mocy. Chociaż epizodyczne głębokie zubożenie warstwy ozonowej miało miejsce w 2023 roku, dane NASA z 2025 roku wskazują na kontynuację długoterminowej odbudowy. W 2025 roku minimalne stężenie ozonu nad Antarktydą wyniosło 147 DU w dniu 6 października, a maksymalny zasięg dziury ozonowej wyniósł 23 · 10⁶ km² w dniu 9 września – około 30% mniej niż największa zarejestrowana dziura. Obserwacje te potwierdzają, że przepisy Protokołu montrealskiego przyczyniają się do stopniowej odbudowy warstwy ozonowej.
Statystyka pobrań
Bibliografia
Kramarova N, Lait LR. Ozone facts [Internet]. Greenbelt (MD): NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Ozone Watch; updated 2024 Sep 23 [cited 2025 Mar 8]. Available from: https://ozonewatch.gsfc.nasa.gov/facts/SH.html. Google Scholar
National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). NASA Ozone Watch [Internet]. Greenbelt (MD): NASA GSFC; 2025 [cited 2025 Mar 8]. Available from: https://ozonewatch.gsfc.nasa.gov/. Google Scholar
National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). Ozone database (1979–present) [Internet]. Greenbelt (MD): NASA GSFC; 2025 [cited 2025 Mar 8]. Available from: https://ozonewatch.gsfc.nasa.gov/meteorology/ytd_data.txt. Google Scholar
National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). Ozone and Air Quality Portal (OMI, OMPS, MLS, SBUV/2, TOMS, GOME) [Internet]. Greenbelt (MD): NASA GSFC; 2025 [cited 2025 Mar 8]. Available from: https://ozoneaq.gsfc.nasa.gov/. Google Scholar
National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). Earthdata [Internet]. Washington (DC): NASA; 2025 [cited 2025 Mar 8]. Available from: https://www.earthdata.nasa.gov/. Google Scholar
National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). GES DISC—Atmospheric Composition Data [Internet]. Greenbelt (MD): NASA GSFC; 2025 [cited 2025 Mar 8]. Available from: https://disc.gsfc.nasa.gov/. Google Scholar
National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). Total Ozone Mapping Spectrometer (TOMS) [Internet]. Washington (DC): NASA Earthdata; 2025 [cited 2025 Mar 8]. Available from: https://www.earthdata.nasa.gov/data/instruments/toms. Google Scholar
National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). TOMS Earth Probe Mission [Internet]. Washington (DC): NASA; 2025 [cited 2025 Mar 8]. Available from: https://science.nasa.gov/mission/toms-ep/. Google Scholar
National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). TOMS ozone archive (since 1978) [Internet]. Greenbelt (MD): NASA GSFC; 2025 [cited 2025 Mar 8]. Available from: https://ozonewatch.gsfc.nasa.gov/data/omto3.html. Google Scholar
National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). Nimbus-7 mission overview [Internet]. Washington (DC): NASA; 2025 [cited 2025 Mar 8]. Available from: https://eospso.nasa.gov/missions/nimbus-7. Google Scholar
National Space Science Data Center (NSSDC). Nimbus satellites and instruments archive [Internet]. Greenbelt (MD): NASA GSFC; 2025 [cited 2025 Mar 8]. Available from: https://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraft.html. Google Scholar
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). SBUV/2 ozone data [Internet]. Asheville (NC): NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information; 2025 [cited 2025 Mar 8]. Available from: https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/products/ozone-sbuv. Google Scholar
National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). Ozone data portal (SBUV/TOMS/OMI/OMPS) [Internet]. Greenbelt (MD): NASA GSFC; 2025 [cited 2025 Mar 8]. Available from: https://ozoneaq.gsfc.nasa.gov/data/ozone/. Google Scholar
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). CLASS: Comprehensive Large Array-data Stewardship System [Internet]. Silver Spring (MD): NOAA; 2025 [cited 2025 Mar 8]. Available from: https://www.class.noaa.gov/. Google Scholar
National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). Aura Mission Overview (OMI, MLS) [Internet]. Greenbelt (MD): NASA GSFC; 2025 [cited 2025 Mar 8]. Available from: https://aura.gsfc.nasa.gov/. Google Scholar
National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) [Internet]. Washington (DC): NASA Earthdata; 2025 [cited 2025 Mar 8]. Available from: https://www.earthdata.nasa.gov/data/instruments/omi. Google Scholar
National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA); Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS) [Internet]. Pasadena (CA): NASA JPL; 2025 [cited 2025 Mar 8]. Available from: https://mls.jpl.nasa.gov/eos-aura-mls/. Google Scholar
National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). Ozone Mapping and Profiler Suite (OMPS) [Internet]. Greenbelt (MD): NASA GSFC; 2025 [cited 2025 Mar 8]. Available from: https://ozoneaq.gsfc.nasa.gov/omps/. Google Scholar
National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). OMPS Nadir Mapper daily L3 data [Internet]. Greenbelt (MD): NASA GSFC; 2025 [cited 2025 Mar 8]. Available from: https://ozonewatch.gsfc.nasa.gov/facts/omps.html. Google Scholar
National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). Suomi NPP Mission [Internet]. Washington (DC): NASA; 2025 [cited 2025 Mar 8]. Available from: https://www.nasa.gov/mission/suomi-npp/. Google Scholar
European Space Agency (ESA). Global Ozone Monitoring Experiment (GOME) [Internet]. Paris: ESA; 2025 [cited 2025 Mar 8]. Available from: https://earth.esa.int/eogateway/instruments/gome. Google Scholar
European Space Agency (ESA). GOME data catalogue [Internet]. Paris: ESA; 2025 [cited 2025 Mar 8]. Available from: https://earth.esa.int/eogateway/catalog/gome. Google Scholar
National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). Upper Atmosphere Research Satellite (UARS) [Internet]. Greenbelt (MD): NASA GSFC; 2025 [cited 2025 Mar 8]. Available from: https://uars.gsfc.nasa.gov/. Google Scholar
National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). MERRA-2 atmospheric reanalysis [Internet]. Greenbelt (MD): NASA GMAO; 2025 [cited 2025 Mar 8]. Available from: https://gmao.gsfc.nasa.gov/reanalysis/MERRA-2/. Google Scholar
National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). GEOS-FP forward processing system [Internet]. Greenbelt (MD): NASA GMAO; 2025 [cited 2025 Mar 8]. Available from: https://gmao.gsfc.nasa.gov/weather_prediction/GEOS-FP/. Google Scholar
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). South Pole balloon-borne ozonesonde program [Internet]. Boulder (CO): NOAA Global Monitoring Laboratory; 2025 [cited 2025 Mar 8]. Available from: https://gml.noaa.gov/ozwv/ozsondes/spo.html. Google Scholar
United Nations. Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer [Internet]. New York: United Nations; 1987 [cited 2025 Mar 8]. Available from: https://treaties.un.org/doc/Publication/UNTS/Volume%201522/volume-1522-I-26369-English.pdf. Google Scholar
United Nations. Vienna Convention for the Protection of the Ozone Layer [Internet]. New York: United Nations; 1985 [cited 2025 Mar 8]. Available from: https://treaties.un.org/doc/Treaties/1988/09/19880922%2003-14%20AM/Ch_XXVII_02p.pdf. Google Scholar
United Nations. London Amendment to the Montreal Protocol [Internet]. New York: United Nations; 1990 [cited 2025 Mar 8]. Available from: https://treaties.un.org/doc/source/events/2016/Publication/publication-English.pdf. Google Scholar
United Nations. Copenhagen Amendment to the Montreal Protocol [Internet]. New York: United Nations; 1992 [cited 2025 Mar 8]. Available from: https://treaties.un.org/doc/source/events/2016/Publication/publication-English.pdf. Google Scholar
United Nations. Montreal Amendment to the Montreal Protocol [Internet]. New York: United Nations; 1997 [cited 2025 Mar 8]. Available from: https://treaties.un.org/doc/source/events/2016/Publication/publication-English.pdf. Google Scholar
United Nations. Beijing Amendment to the Montreal Protocol [Internet]. New York: United Nations; 1999 [cited 2025 Mar 8]. Available from: https://treaties.un.org/doc/source/events/2016/Publication/publication-English.pdf. Google Scholar
United Nations. Kigali Amendment to the Montreal Protocol [Internet]. New York: United Nations; 2016 [cited 2025 Mar 8]. Available from: https://treaties.un.org/doc/Treaties/2016/10/20161015%2003-23%20PM/Ch_XXVII-2.f-English%20and%20French.pdf. Google Scholar
European Union. Regulation (EC) No 1005/2009 on substances that deplete the ozone layer [Internet]. Official Journal of the European Union; 2009 [cited 2025 Mar 8]. Available from: https://www.eea.europa.eu/policy-documents/regulation-ec-1005-2009-on. Google Scholar
European Union. Regulation (EU) No 517/2014 on fluorinated greenhouse gases [Internet]. Official Journal of the European Union; 2014 [cited 2025 Mar 8]. Available from: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2014/517/. Google Scholar
World Meteorological Organization, United Nations Environment Programme. Scientific Assessment of Ozone Depletion: 2018. Global Ozone Research and Monitoring Project–Report No. 58. Geneva: WMO; 2018. Google Scholar
European Union. Regulation (EU) 2024/573 on fluorinated greenhouse gases [Internet]. Official Journal of the European Union; 2024 [cited 2025 Mar 8]. Available from: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2024/573/. Google Scholar
European Union. Regulation (EU) 2021/1119 establishing the European Climate Law [Internet]. Official Journal of the European Union; 2021 [cited 2025 Mar 8]. Available from: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2021/1119/. Google Scholar
United Nations Environment Programme. Thirty years on, what is the Montreal Protocol doing to protect the ozone? [Internet]. Nairobi: UNEP; 2019 Nov 15 [cited 2025 Mar 8]. Available from: https://www.unep.org/news-and-stories/story/thirty-years-what-montreal-protocol-doing-protect-ozone. Google Scholar
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration; National Aeronautics and Space Administration. 2025 ozone hole is 5th smallest since 1992 [Internet]. Washington (DC): NOAA; 2025 Nov 24 [cited 2025 Mar 8]. Available from: https://www.noaa.gov/news-release/noaa-nasa-2025-ozone-hole-is-5th-smallest-since-1992. Google Scholar
Pobrania
Opublikowane
Jak cytować
Numer
Dział
Licencja
Prawa autorskie (c) 2025 Agnieszka Lisowska-Lis

Utwór dostępny jest na licencji Creative Commons Uznanie autorstwa – Na tych samych warunkach 4.0 Miedzynarodowe.



