Przegląd rozwiązań zastosowanych w urządzeniach rehabilitacyjnych wykorzystujących muskuły i siłowniki pneumatyczne
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5604/01.3001.0014.7532Słowa kluczowe:
siłowniki pneumatyczne, muskuły pneumatyczne, urządzenia rehabilitacyjneAbstrakt
W artykule przedstawiono wybrane urządzenia rehabilitacyjne z zastosowaniem klasycznych siłowników oraz muskułów pneumatycznych. Zaprezentowano manipulatory wspomagające ruchy kończyn dolnych i górnych człowieka. Ponadto opisano budowę siłowników i muskułów pneumatycznych.
Statystyka pobrań
Bibliografia
Aschemann H, Schindele D. Comparison of model-based approaches to the compensation of hysteresis in the force characteristic of pneumatic muscles. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics. 2014;61(7):3620–3629. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2013.2287217. Google Scholar
Bharadwaj K, Sugar T. Kinematics of a robotic gait trainer for stroke. In: Proceedings 2006 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2006. Orlando, FL: ICRA; 2006. p. 3492–3497. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ROBOT.2006.1642235. Google Scholar
Caldwell DG, Razak A, Goodwin MJ. Braided pneumatic muscle actuators. IFAC Proceedings Volumes. 1993;26(1):507–512. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-6670(17)49354-2. Google Scholar
Cao J, Xie SQ, Das R. MIMO sliding mode controller for gait exoskeleton driven by pneumatic muscles. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology. 2018;26(1):274–281. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TCST.2017.2654424. Google Scholar
Choi TY, Lee JJ. Control of manipulator using pneumatic muscles for enhanced safety. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics. 2010;57(8): 2815–2825. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2009.2036632. Google Scholar
Dindorf R. Rozwój zaopatrzenia ortopedycznego z elementami płynowymi. Pomiary, Automatyka, Robotyka. 2004;7(6): 4–9. Google Scholar
Sugar TG, et al. Design and control of RUPERT: a device for Robotic Upper Extremity Repetitive Therapy. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering. 2007;15(3):336–346. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSRE.2007.903903. Google Scholar
Forducey P, Hentz V, Burdea G, Fensterheim D, Winter S, Kourtev H, Heuser A. Tele-rehabilitation using the Rutgers Master II glove following carpal tunnel release surgery. In: 2006 International Workshop on Virtual Rehabilitation. New York, NY: IEEE; 2006. p. 88–93. https://doi.org/10.1109/IWVR.2006.1707533. Google Scholar
Holt R, et al. User involvement in developing rehabilitation robotic devices: an essential requirement. In: 2007 IEEE 10th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics. Noordwijk: IEEE; 2007. p. 196-204. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICORR.2007.4428427. Google Scholar
Sarakoglou I, Kousidou S, Tsagarakis NG, Caldwell DG. Exoskeleton-based exercisers for the disabilities of the upper arm and hand. In: Kommu SS, editor. Rehabiliatation Robotics. Vienna: Itech Education and Publishing; 2007. p. 500–522. doi: https://doi.org/10.5772/5177. Google Scholar
Sanchez RJ, et al. A pneumatic robot for re-training arm movement after stroke: rationale and mechanical design. In: 9th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, 2005. ICORR 2005. Chicago: IEEE; 2005. p. 500–504. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICORR.2005.1501151. Google Scholar
Szenajch W. Napęd i sterowanie pneumatyczne. Warszawa: Wydawnictwa Naukowo-Techniczne; 1997. Google Scholar
Takosoglu JE, Laski PA, Blasiak S, Bracha G, Pietrala D. Determining the static characteristics of pneumatic muscles. Measurement and Control. 2016;49(2):62–71. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/0020294016629176. Google Scholar
Company advertising materials Flowtron HYDROVEN – PPU Real Olsztyn. Google Scholar
Hand rehabilitation system / computer-based Hand Mentor Kinetic Muscles. [Internet]. Available from: https://healthmanagement.org/products/view/hand-rehabilitation-system-computer-based-hand-mentor-kinetic-muscles. Accessed 15 January 2021. Google Scholar
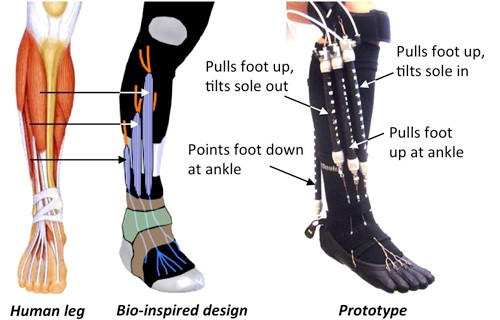
Spice B. Press relase: bio-inspired robotic device could aid ankle-foot rehabilitation, CMU researcher says. [Internet].Available from: https://www.cmu.edu/news/stories/archives/2014/january/jan20_anklefootrehab.html. Published 20 January 2014. Accessed 20 January 2021. Google Scholar
EBMiA.pl Elementy Budowy Maszym i Automatyki. [website]. Available from: www.ebmia.pl. Accessed 2 February 2021. Google Scholar
Muskuł pneumatyczny MAS I DMSP. [Internet]. Available from: https://www.automatyka.pl/produkty/muskul-pneumatyczny-mas-i-dmsp-7673-2. Published 18 May 2006. Accessed 4 February 2021. Google Scholar
Fluidic muscle DMSP. Festo; 2019. [Internet]. Available from: https://www.festo.com/cat/pl_pl/data/doc_engb/PDF/EN/DMSP_EN.PDF. Accessed 17 February 2021. Google Scholar
Pobrania
Opublikowane
Jak cytować
Numer
Dział
Licencja
Prawa autorskie (c) 2020 Państwowa Wyższa Szkoła Zawodowa w Tarnowie & Autorzy

Utwór dostępny jest na licencji Creative Commons Uznanie autorstwa – Użycie niekomercyjne 4.0 Międzynarodowe.



