Research and determination of the degradation mechanism of repeatedly processed polycarbonate
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5604/01.3001.0014.8185Keywords:
polycarbonate, material recycling, physical properties of polycarbonate, degradation of polycarbonateAbstract
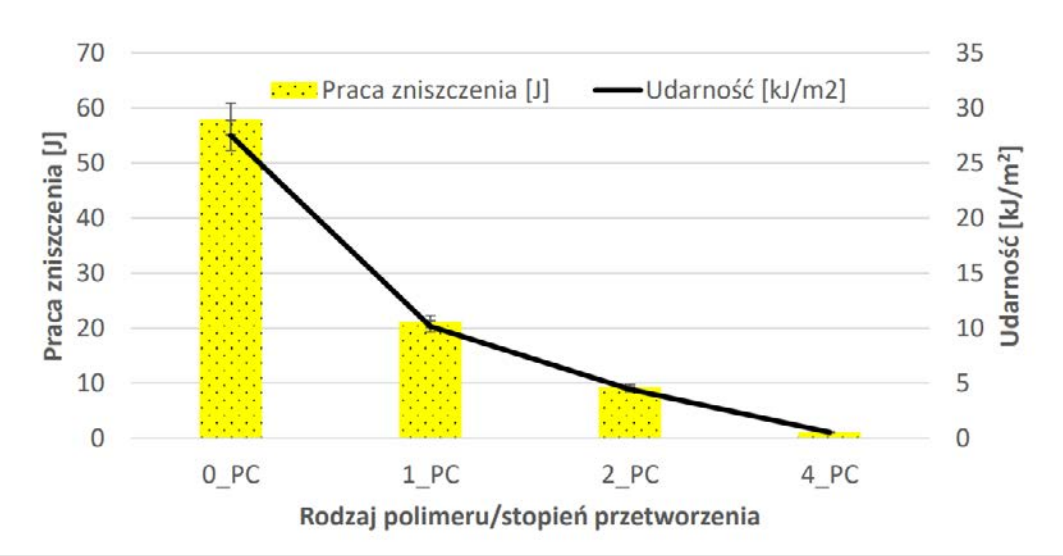
The difficulty of processing thermoplastics at the end of lifecycle or post-production waste is very important for saving environment. Every year, tons of new raw polycarbonate thermoplastic grades (PC), are introduced to the market. Unfortunately, despite the theoretical possibility of recycling and reusing thermoplastics, polycarbonate recyclates are not popular on the market and they are wasted. The paper investigates and presents the relationships and changes in the mechanical properties as a function of the multiple processing of post-production polycarbonate panel waste. The possible types of plastic degradation during processing and its influence on the decrease of mechanical parameters ware investigated.
Downloads
References
Pickering SJ. Recycling technologies for thermoset composite materials – current status. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing. 2006;37(8):1206–1215. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2005.05.030. Google Scholar
Jacob A. Composites can be recycled. Reinforced Plastics. 2011;55(3):45–46. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0034-3617(11)70079-0. Google Scholar
Oliveux G, Dandy LO, Leeke GA. Current status of recycling of fibre reinforced polymers: review of technologies, reuse and resulting properties. Progress in Materials Science. 2015;72:61–99. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2015.01.004. Google Scholar
Cui J, Forssberg E. Mechanical recycling of waste electric and electronic equipment: a review. Journal of Hazardous Materials. 2003;99(3):243–263. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3894(03)00061-X. Google Scholar
Uyar T, Tonelli AE, Hacaloğlu J. Thermal degradation of polycarbonate, poly(vinyl acetate) and their blends. Polymer Degradation and Stability. 2006;91(12):2960–2967. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2006.08.028. Google Scholar
Xiao J, Chen Y, Wang S, Lu P, Hu Y. Thermal degradation mechanism of polycarbonate/organically modified montmorillonite nanocomposites. Polymer Composites. 2016;37:2301–2305. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.23408. Google Scholar
Rydzkowski T. Teoretyczne i doświadczalne podstawy efektywnego wytłaczania ślimakowo-tarczowego w recyklingu materiałów i kompozytów polimerowych. Koszalin: Wydawnictwo Uczelniane Politechniki Koszalińskiej; 2012. Google Scholar
Booth C. The mechanical degradation of polymers. Polymer. 1963;4:471–478. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/0032-3861(63)90060-0. Google Scholar
Elmaghor F, Zhang L, Fan R, Li H. Recycling of polycarbonate by blending with maleic anhydride grafted ABS. Polymer. 2004;45(19):6719–6724. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2004.07.022. Google Scholar
Fraïsse F, Verney V, Commereuc S, Obadal M. Recycling of poly(ethylene terephthalate) / polycarbonate blends. Polymer Degradation and Stability. 2005;90(2):250–255. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2005.02.019. Google Scholar
Hidaka K, Iwakawa Y, Maoka T, Tanimoto F, Oku A. Viable chemical recycling of poly(carbonate) as a phosgene equivalent illustrated by the coproduction of bisphenol A and carbohydrate carbonates. Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management. 2009;11:6–10. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-008-0211-7. Google Scholar
De la Colina Martínez AL, Martínez Barrera G, Barrera Díaz CE, Ávila Córdoba LI, Ureña Núñez F, Delgado Hernández DJ. Recycled polycarbonate from electronic waste and its use in concrete: effect of irradiation. Construction and Building Materials. 2019;201:778–785. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.12.147. Google Scholar
Rabek JF. Podstawy fizykochemii polimerów. Wrocław: Wydawnictwo Politechniki Wrocławskiej; 1977. Google Scholar
Żuchowska D. Polimery konstrukcyjne: wprowadzenie do technologii i stosowania. Warszawa: Wydawnictwa Naukowo-Techniczne; 1995. Google Scholar
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2020 University of Applied Sciences in Tarnow, Poland & Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.



