Overview of solutions used in rehabilitation devices using muscles and pneumatic actuators
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5604/01.3001.0014.7532Keywords:
pneumatic actuators, pneumatic muscle, rehabilitation devicesAbstract
The article presents selected rehabilitation devices with the use of classic actuators and pneumatic muscles. Manipulators supporting the movements of the lower and upper limbs of humans are presented. Moreover, the construction of actuators and pneumatic muscles is described.
Downloads
References
Aschemann H, Schindele D. Comparison of model-based approaches to the compensation of hysteresis in the force characteristic of pneumatic muscles. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics. 2014;61(7):3620–3629. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2013.2287217. Google Scholar
Bharadwaj K, Sugar T. Kinematics of a robotic gait trainer for stroke. In: Proceedings 2006 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2006. Orlando, FL: ICRA; 2006. p. 3492–3497. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ROBOT.2006.1642235. Google Scholar
Caldwell DG, Razak A, Goodwin MJ. Braided pneumatic muscle actuators. IFAC Proceedings Volumes. 1993;26(1):507–512. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-6670(17)49354-2. Google Scholar
Cao J, Xie SQ, Das R. MIMO sliding mode controller for gait exoskeleton driven by pneumatic muscles. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology. 2018;26(1):274–281. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TCST.2017.2654424. Google Scholar
Choi TY, Lee JJ. Control of manipulator using pneumatic muscles for enhanced safety. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics. 2010;57(8): 2815–2825. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2009.2036632. Google Scholar
Dindorf R. Rozwój zaopatrzenia ortopedycznego z elementami płynowymi. Pomiary, Automatyka, Robotyka. 2004;7(6): 4–9. Google Scholar
Sugar TG, et al. Design and control of RUPERT: a device for Robotic Upper Extremity Repetitive Therapy. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering. 2007;15(3):336–346. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSRE.2007.903903. Google Scholar
Forducey P, Hentz V, Burdea G, Fensterheim D, Winter S, Kourtev H, Heuser A. Tele-rehabilitation using the Rutgers Master II glove following carpal tunnel release surgery. In: 2006 International Workshop on Virtual Rehabilitation. New York, NY: IEEE; 2006. p. 88–93. https://doi.org/10.1109/IWVR.2006.1707533. Google Scholar
Holt R, et al. User involvement in developing rehabilitation robotic devices: an essential requirement. In: 2007 IEEE 10th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics. Noordwijk: IEEE; 2007. p. 196-204. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICORR.2007.4428427. Google Scholar
Sarakoglou I, Kousidou S, Tsagarakis NG, Caldwell DG. Exoskeleton-based exercisers for the disabilities of the upper arm and hand. In: Kommu SS, editor. Rehabiliatation Robotics. Vienna: Itech Education and Publishing; 2007. p. 500–522. doi: https://doi.org/10.5772/5177. Google Scholar
Sanchez RJ, et al. A pneumatic robot for re-training arm movement after stroke: rationale and mechanical design. In: 9th International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, 2005. ICORR 2005. Chicago: IEEE; 2005. p. 500–504. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICORR.2005.1501151. Google Scholar
Szenajch W. Napęd i sterowanie pneumatyczne. Warszawa: Wydawnictwa Naukowo-Techniczne; 1997. Google Scholar
Takosoglu JE, Laski PA, Blasiak S, Bracha G, Pietrala D. Determining the static characteristics of pneumatic muscles. Measurement and Control. 2016;49(2):62–71. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/0020294016629176. Google Scholar
Company advertising materials Flowtron HYDROVEN – PPU Real Olsztyn. Google Scholar
Hand rehabilitation system / computer-based Hand Mentor Kinetic Muscles. [Internet]. Available from: https://healthmanagement.org/products/view/hand-rehabilitation-system-computer-based-hand-mentor-kinetic-muscles. Accessed 15 January 2021. Google Scholar
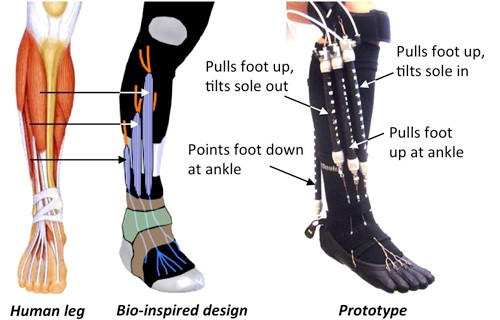
Spice B. Press relase: bio-inspired robotic device could aid ankle-foot rehabilitation, CMU researcher says. [Internet].Available from: https://www.cmu.edu/news/stories/archives/2014/january/jan20_anklefootrehab.html. Published 20 January 2014. Accessed 20 January 2021. Google Scholar
EBMiA.pl Elementy Budowy Maszym i Automatyki. [website]. Available from: www.ebmia.pl. Accessed 2 February 2021. Google Scholar
Muskuł pneumatyczny MAS I DMSP. [Internet]. Available from: https://www.automatyka.pl/produkty/muskul-pneumatyczny-mas-i-dmsp-7673-2. Published 18 May 2006. Accessed 4 February 2021. Google Scholar
Fluidic muscle DMSP. Festo; 2019. [Internet]. Available from: https://www.festo.com/cat/pl_pl/data/doc_engb/PDF/EN/DMSP_EN.PDF. Accessed 17 February 2021. Google Scholar
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2020 University of Applied Sciences in Tarnow, Poland & Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.



