Electrical machines with switched and modulated flux
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5604/01.3001.0013.8981Keywords:
flux switching machine, hybrid excitation, modulated flux machine, induction motorAbstract
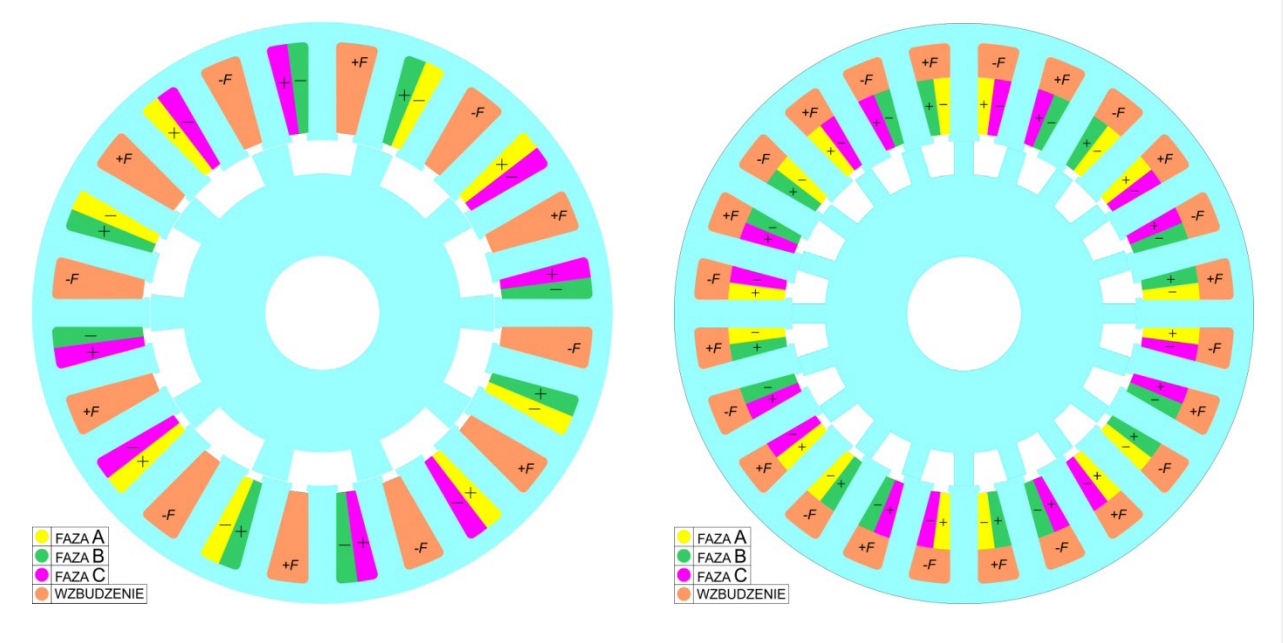
The work compares the value of the produced torque (average value) of a 2.2kW squirrel cage induction motor with new construction machines, i.e. a motor with flux switching and hybrid excitation or DC excited, a motor with flux modulation and hybrid excitation or DC excitation. The external dimensions of the tested machines corresponded to the dimensions of the induction motor.
Downloads
References
Sobczyk TJ. Problemy modelowania matematycznego prądnic synchronicznych wzbudzanych magnesami trwałymi. Prace instytutu elektrotechniki. 2007;231:99-123. Google Scholar
Hoang E, Lecrivain M, Gabsi M, inventors. CNRS, assignee. Machine électrique a commutation de flux et a double excitation. International Patent FR0602058. 2007-03-08. Google Scholar
Hoang E, Lecrivain M, Gabsi M.A new structure of a switching flux synchronous polyphased machine with hybrid excitation. Proceedings of the2007 European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications; 2007 Sep 2-5; Aalbork, Denmark. IEEE; 2008, pp. 1–8. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/EPE.2007.4417204. Google Scholar
Hoang E, Lécrivain M, Hlioui S, Gabsi M. Hybrid excitation synchronous permanent magnets synchronous machines optimally designed for hybrid and full electrical vehicle. Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Power Electronics – ECCE Asia; 2011 May 30 – Jun 3; Jeju, South Korea. IEEE; 2011, pp. 153–160. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICPE.2011.5944569. Google Scholar
Hoang E, Ben-Ahmed AH, Lucidarme J. Switching flux permanent magnet polyphased synchronous machines. Proceedings of the 7th European Conference on Power Electron Application; 1997 Sep 8-10; Trondheim, Norway. EPE Association; 1997, vol. 3, pp. 903–908. Google Scholar
Chen JT, Zhu ZQ,Iwasaki S, Deodhar R. Low Cost Flux-Switching Brushless AC Machines. Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference; 2010 Sep 1-3; Lille, France. IEEE; 2011, pp. 1–6. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/VPPC.2010.5728984. Google Scholar
Sulaiman E, Kosaka T, Matsui N. A new structure of 12Slot10Pole field-excitation flux switching synchronous machine for hybrid electric vehicles. Proceedings of the 2011 14th European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications; 2011 Aug 30 – Sep 1; Birmingham, UK. IEEE; 2011, pp. 1–10. Google Scholar
Pollock C,Wallace M.The flux switching motor, a DC motor without magnets or brushes. Conference Record of the 1999 IEEE Industry Applications Conference. Thirty-Forth IAS Annual Meeting (Cat. No.99CH36370); 1999 Oct 3-7; Phoenix, AZ, USA. IEEE; 2002, vol.3, pp.1980-1987. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/IAS.1999.806009. Google Scholar
Tang Y, Ilhan E, Paulides JJH, Lomonova EA. Design considerations of flux-switching machines with permanent magnet or DC excitation. Proceedings of the2013 15th European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications (EPE); 2013 Sep 2-6; Lille, France. IEEE; 2013, pp. 1–10. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/EPE.2013.6634396. Google Scholar
Tang Y, Paulides JJH, Lomonova EA. Field weakening performance of flux-switching machines for hybrid/electric vehicles. Proceedings of the 2015-Tenth International Conference on Ecological Vehicles and Renewable Energies (EVER), 2015 Mar 31 – Apr 2; Monte Carlo, Monaco. IEEE; 2015, pp. 1-10. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/EVER.2015.7112995. Google Scholar
Gao Y, Qu R, Li D, Li J. A Novel Hybrid Excitation Flux Reversal Machine for Electric Vehicle Propulsion. Proceedings of the 13th IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference (VPPC); 2016Oct 17-20; Hangzhou, China. IEEE; 2016, pp. 1–6. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/VPPC.2016.7791585. Google Scholar
Boldea I, Serban E, Babau R. Flux reversal stator-PM single-phase generator with controlled DC output. Record of OPTIM-96; 1996 May; Brasov, Romania. pp. 1123-1137. Google Scholar
Deodhar RP, Andersson S, Boldea I, Miller TJE. The flux-reversal machine: anew brushless doubly-salient permanent-magnet machine. IAS ‘96. Conference Record of the 1996 IEEE Industry Applications Conference Thirty-First IAS Annual Meeting; 1996 Oct 6-10; San Diego, CA, USA. IEEE; 2002, vol. 2, pp. 786 – 793. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/IAS.1996.560174. Google Scholar
Gao Y, Qu R, Li D, Li J. Design and comparison of novel flux reversal machines with large stator slot opening. Proceedings of the2016 IEEE Conference on Electromagnetic Field Computation (CEFC); 2016 Nov 13-16; Miami, FL, USA. IEEE; 2017, pp. 1-1. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/CEFC.2016.7816195. Google Scholar
Gao Y, Qu R, Li D, Li J. Design procedure of flux reversal permanent magnet machines. Proceedings of the 2016 XXII International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM); 2016 Sep 4-7; Lausanne, Switzerland. IEEE; 2016, pp. 1584–1590. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICELMACH.2016.7732735. Google Scholar
Gao Y, Li D, Qu R, Li J. Design procedure of flux reversal permanent magnet machines. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications. 2017;53(5):4232–4241. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TIA.2017.2695980. Google Scholar
Fukami T, Matsuura Y, Shima K, Momiyama M, Kawamura M. Development of a low-speed multi-pole synchronous machine with a field winding on the stator side. Proceedings of the XIX International Conference on Electrical Machines - ICEM 2010; 2010 Sep 6-8; Rome, Italy. IEEE; 2010, pp. 1-6, doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICELMACH.2010.5608212. Google Scholar
Fukami T, Momiyama M, Shima K, Hanaoka R, Takata S. Steady-State Analysis of a Dual-Winding Reluctance Generator With a Multiple-Barrier Rotor. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion. 2008;23(2):492–498. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/TEC.2008.918656. Google Scholar
http://www.femm.info/wiki/HomePage. Google Scholar
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2020 University of Applied Sciences in Tarnow, Poland & Authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.



