State Higher Vocational School Weather Station in Tarnów
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5604/01.3001.0010.7618Abstract
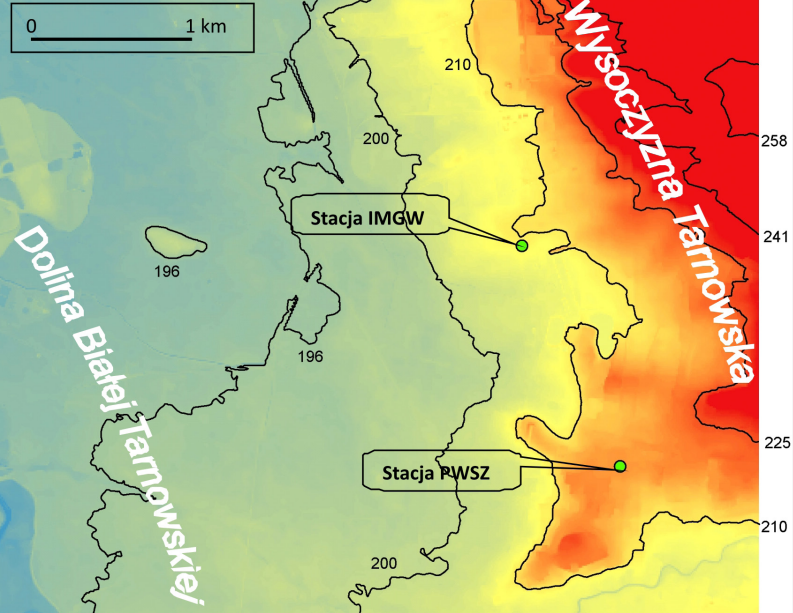
In 2015 the State Higher Vocational School in Tarnów (PWSZ), under the Norwegian Project implemented in the Department of Environmental Protection, purchased and set in motion semi-professional automatic weather station DAVIS Vantage Pro2. The station measures basic meteorological elements e.g. air temperature, wind speed and direction or solar radiation. The logged data are intended for teaching at the School, including the specialization of environmental protection. Comparison of the data acquired at the PWSZ station and at the synoptic station of Institute of Meteorology and Water Management (IMGW) allowed the evaluation of the correlation of the measurement series of both stations. Furthermore it allowed for the initial analysis of the urban heat island (MWC) as one of the aspects of the local climate. There are confirmed typical thermal marks of the urban heat island during favourable weather conditions with radiation cooling at night. Especially during cloudless and windless radiation night, the air cools down more at the rural areas, and this favours the occurrence of the urban heat island phenomenon. The urban – rural thermal contrasts are then the greatest, up to 3°C. In the daytime difference between the centre and the outskirts of the city is quite small (under 1°C), so generally the urban heat island doesn’t occur during the day.
Downloads
References
Bac S., Koźmiński C., Rojek M., Agrometeorologia, Wyd. Nauk. PWN, Warszawa, 1993, s. 178–190, 214–215, 219–223. Google Scholar
Błażejczyk K., Kuchcik M., Milewski P., Dudek W., Kręcisz B., Błażejczyk A., Szmyd J., Degórska B., Pałczyński C. M., Miejska wyspa ciepła w Warszawie: uwarunkowania klimatyczne i urbanistyczne, Wyd. Akadem. SEDNO, Warszawa, 2014, s. 9–11, 39–47. Google Scholar
Fortuniak K., Miejska wyspa ciepła, Wyd. Uniwersytetu Łódzkiego, Łódź, 2003, s. 13–27. Google Scholar
Gabała J., Kühne O., Distribution of air pollution and its microclimatological conditioning with Tarnów City as an example. Instytut Geografii i Gospodarki Przestrzennej Uniwersytetu Jagiellońskiego, Kraków, 2003, s. 66–68. Google Scholar
Geoportal, http://mapy.geoportal.gov.pl/imap/?gpmap=gp3; Odsłona 15.05.2017 r. Google Scholar
Giża K., Rozkład wybranych elementów pogodowych podczas nocy radiacyjnych w Tarnowie, Praca licencjacka, Maszynopis, PWSZ w Tarnowie, Tarnów, 2012. Google Scholar
Hanik J., Stacja meteorologiczna w Tarnowie, Gazeta Obserwatora P.I.H.M., Rok XII, 6(138), 1959, str. 10–11. Google Scholar
Helbig A., Baumüller J., Kerschgens M., Stadtklima und Luftreinhaltung, Springer Verlag, Berlin – Heidelberg – New York, 1999, s. 32–37. Google Scholar
IMGW – PIB, https://dane.imgw.pl/; Źródłem pochodzenia danych jest IMGW – Państwowy Instytut Badawczy; odsłony IV i V 2017 r. Google Scholar
Klejnowski R., 2016a. Komentarz synoptyka z dnia 19 sierpnia 2016 r. http://www.meteo.pl/komentarze/index1.php?date=2016-08-19; Odsłona10.05.2017 r. Google Scholar
Klejnowski R., 2016b. Komentarz synoptyka z dnia 20 sierpnia 2016 r. http://www.meteo.pl/komentarze/index1.php?date=2016-08-20; Odsłona10.05.2017 r. Google Scholar
Kossowska-Cezak U., Marty D., Olszewski K., Kopacz-Lembowicz M., Meteorologia i klimatologia. Pomiary, obserwacje, opracowania, Wyd. Nauk. PWN, Warszawa – Łódź, 2000, s. 40–43, 219–220. Google Scholar
Landsberg H., The Urban Climate, Academic Press, New York, 1981, s. 83–112. Google Scholar
Lewińska J., Klimat miasta, zasoby, zagrożenia, kształtowanie, Instytut Gospodarki Przestrzennej i Komunalnej, Kraków, 2000. Google Scholar
Ostrowski M., 2017, Komentarz synoptyka z dnia 28 stycznia 2017 r. http://www.meteo.pl/komentarze/index1.php?date=2017-01-28; Odsłona 11.05.2017 r. Google Scholar
Pawlik F., Wybrane cechy klimatu lokalnego w czasie nocy radiacyjnych w południowo-zachodniej części Tarnowa i w Koszycach Wielkich, Praca licencjacka, Maszynopis, PWSZ w Tarnowie, Tarnów, 2015. Google Scholar
Piwkowski H., 2017, Komentarz synoptyka z dnia 29 stycznia 2017 r. http://www.meteo.pl/komentarze/index1.php?date=2017-01-29; Odsłona 11.05.2017 r. Google Scholar
Purchla J., Objaśnienia do Szczegółowej Mapy Geologicznej Polski, Arkusz Tarnów (997), Wyd. PIG, Warszawa, 1994. Google Scholar
Suwała S., Wybrane cechy klimatu lokalnego rejonu Zakładów Azotowych w Tarnowie-Mościcach, Praca licencjacka, Maszynopis, PWSZ w Tarnowie, Tarnów, 2010. Google Scholar
WIOŚ Kraków, Małopolskie – System Monitoringu Jakości Powietrza; http://monitoring.krakow.pios.gov.pl/dane-pomiarowe/automatyczne/stacja/150/parametry/1728-1730-1727-1732-1729/dzienny/04.01.2016; Odsłona 10.05.2017 r. Google Scholar
Wyszkowski A., Przewodnik do ćwiczeń terenowych z meteorologii i klimatologii, Wydawnictwo Uniwersytetu Gdańskiego, Gdańsk, 2008, s. 144–151. Google Scholar
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2017 University of Applied Sciences in Tarnow, Poland & Author

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.



